Product Description
Products Description
|
Product Name |
Diff Rear End Assy |
|||
|
Brand |
CHINAMFG |
|||
|
Material |
Aluminum |
|||
|
Quality |
100% Test |
|||
|
Part Number |
41300-HP0-B80 41300-HP0-A00 |
|||
|
OEM number |
41300HP0B80 41300HP0A00 |
|||
|
OE number |
41300 HP0 B80 |
|||
|
Size |
OEM Standard |
|||
Details Images
Our Advantages-Why Choose Us
Transport
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are the set design, development, production, sale and service of industry and trade-oriented enterprises.
Q: What is the MOQ?
A: MOQ depends on our clients demands, we welcome trial order before mass production.
Q: How does your factory make sure the product quality?
A: Durning production, we have FQC, IQC ,IPQC and OQC to control the quality. We will final check before shipping to avoid any problem.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: T/T, paypal, ali-pay,west union, cash, etc, paid before shippment.
Q:What is the warranty?
A:One year for CHINAMFG parts and 3 years for OEM parts.
Q:Can you send products to my country?
A:Sure,we can. We can ship the goods by express or by sea.
Q:Can you do OEM for me?
A: We accept OEM and ODM.
Q: How can I place the order?
A: Confirm PI or Invoice, make payment, then we will arrange shipment soon.
Q: When can I get the quotation ?
A: We usually quote you within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the quotation.Please call us or tell us in your mail, so that we could regard your inquiry priority.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1year |
| Size: | OE Standard, OEM Standard |
| Car Fitment: | Honda |
| Product Name: | Diff Rear End Assy |
| OE Number: | 41300-HP0-B80 41300-HP0-A00, Wg1249357 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
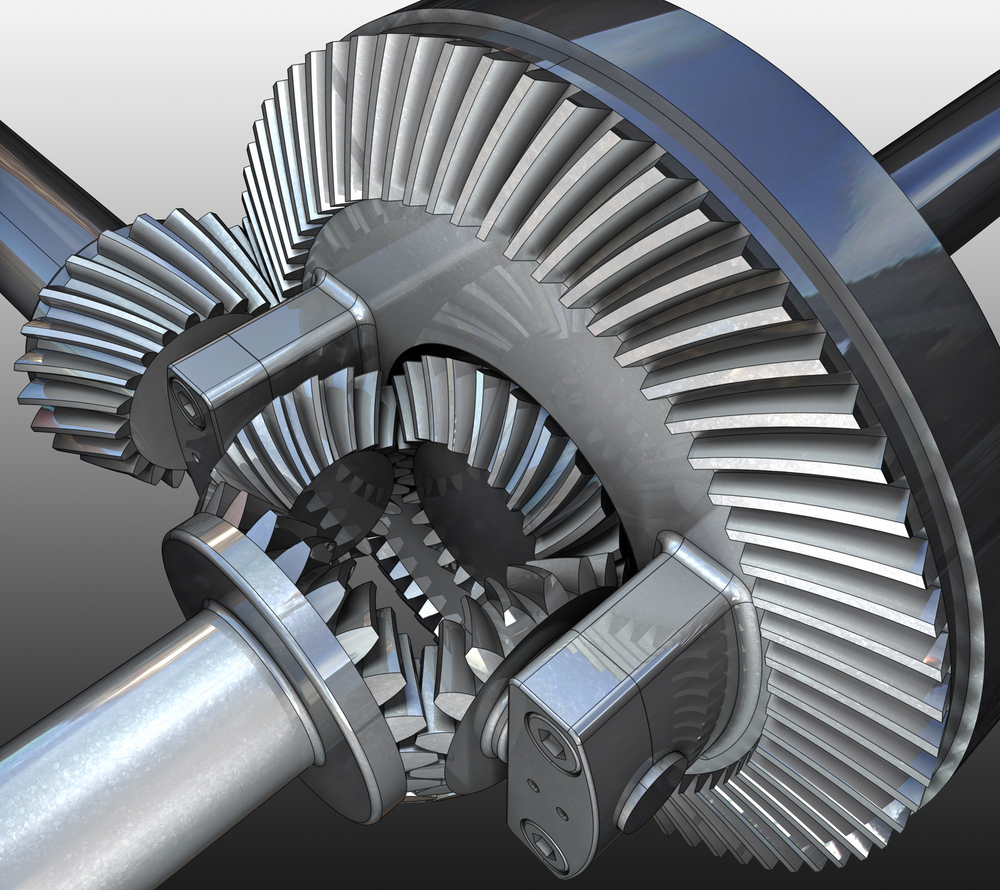
What is the impact of a malfunctioning differential gear on a vehicle’s performance?
A malfunctioning differential gear can significantly impact a vehicle’s performance and drivability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the effects of a malfunctioning differential gear:
1. Limited Traction:
A malfunctioning differential gear may result in limited traction, especially in off-road or slippery conditions. The differential gear distributes torque between the wheels to provide optimal traction. If the gear malfunctions, it may not distribute power evenly, causing one or more wheels to lose traction. This can result in wheel slip, difficulty in accelerating, and compromised control over the vehicle.
2. Poor Handling and Stability:
The differential gear plays a critical role in maintaining stability and handling characteristics of a vehicle. A malfunctioning differential gear can disrupt the balance between the wheels, leading to poor handling and stability. For example, if a rear-wheel-drive vehicle’s differential gear fails, it can cause excessive oversteer or understeer, making the vehicle difficult to control during cornering or sudden maneuvers.
3. Increased Tire Wear:
A malfunctioning differential gear can cause uneven tire wear. When the gear fails to distribute torque evenly, some wheels may experience excessive slippage or spinning, while others receive insufficient power. This uneven distribution of forces can lead to accelerated tire wear on specific wheels, resulting in uneven tread wear patterns and reducing the overall lifespan of the tires.
4. Abnormal Noise and Vibration:
A malfunctioning differential gear can produce abnormal noises and vibrations. If the gear’s components, such as bearings or gears, wear out or become damaged, it can result in grinding, whining, or clunking noises during operation. Additionally, the vehicle may experience vibrations, especially when accelerating or navigating turns. These symptoms indicate potential issues with the differential gear that require immediate attention.
5. Loss of Power and Performance:
A malfunctioning differential gear can lead to a loss of power and performance. If the gear fails to transfer torque effectively, the vehicle may experience reduced power delivery to the wheels. This can result in sluggish acceleration, decreased towing or hauling capacity, and overall compromised performance. The vehicle may struggle to climb inclines, navigate challenging terrain, or maintain speed efficiently.
6. Increased Fuel Consumption:
A malfunctioning differential gear can contribute to increased fuel consumption. When the gear fails to distribute torque properly, the engine may need to work harder to compensate for the lack of power transmission. This increased workload can lead to higher fuel consumption, as the engine consumes more fuel to maintain performance levels.
7. Safety Concerns:
A malfunctioning differential gear can pose safety concerns for the driver and passengers. Limited traction, poor handling, and compromised stability increase the risk of accidents, especially in adverse weather conditions or emergency situations. It is crucial to address any differential gear issues promptly to ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.
In summary, a malfunctioning differential gear can have a significant impact on a vehicle’s performance. It can result in limited traction, poor handling and stability, increased tire wear, abnormal noises and vibrations, loss of power and performance, increased fuel consumption, and safety concerns. Regular maintenance, prompt repairs, and addressing differential gear issues can help maintain the vehicle’s performance, drivability, and overall safety.
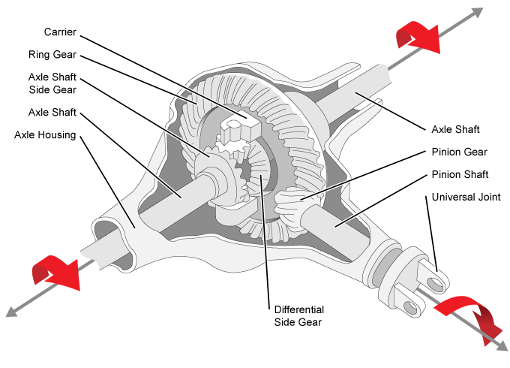
What is the process for diagnosing and repairing a differential gear issue?
Diagnosing and repairing a differential gear issue involves several steps to identify the problem accurately and implement the necessary repairs. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process:
- Initial Inspection: The process begins with a visual inspection of the differential gear assembly and surrounding components. This includes checking for any signs of leaks, damage, or abnormal wear. The technician will also listen for unusual noises, such as grinding, whining, or clunking sounds, which can indicate potential issues.
- Fluid Inspection: The next step is to inspect the differential gear oil. The technician will check the fluid level and condition. Contaminated or low fluid levels can contribute to differential problems. If the fluid appears dirty, metallic, or has a burnt smell, it may indicate internal damage or excessive wear.
- Test Drive: A test drive is often conducted to observe the vehicle’s behavior and confirm the presence of any differential gear issues. The technician will pay attention to abnormal noises, vibrations, or handling characteristics that may point to specific problems within the differential assembly.
- Differential Disassembly: If a differential issue is suspected, the technician may need to disassemble the differential assembly for a more detailed inspection. This involves removing the driveshaft, axles, and other components to gain access to the differential gears. The differential housing and gears are carefully inspected for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Measurement and Evaluation: Precision measurements are taken to assess the condition of the differential gears, bearings, and related components. This may involve using specialized tools to check gear backlash, gear tooth wear, bearing clearances, and other critical parameters. These measurements help determine the extent of the problem and whether components need to be repaired or replaced.
- Component Repair or Replacement: Based on the evaluation, the technician will determine the appropriate repair or replacement actions. Damaged or worn components such as gears, bearings, seals, or shims may need to be replaced. In some cases, the entire differential assembly may need to be replaced if the damage is extensive or the cost of repairs outweighs replacement.
- Reassembly and Adjustment: Once the necessary repairs or replacements have been made, the differential assembly is reassembled with new components. Proper adjustments are made to ensure correct gear meshing, preload, and backlash. The technician will also refill the differential with the recommended fluid and perform any additional adjustments or calibrations as required.
- Final Testing: After reassembly, a final test drive is conducted to verify that the differential gear issue has been successfully resolved. The technician will listen for abnormal noises, monitor handling characteristics, and assess overall performance to ensure proper functionality of the repaired differential.
In summary, diagnosing and repairing a differential gear issue involves an initial inspection, fluid inspection, test drive, differential disassembly, measurement and evaluation, component repair or replacement, reassembly and adjustment, and final testing. This systematic process helps identify the problem, determine the necessary repairs, and restore the differential gear to proper working condition.
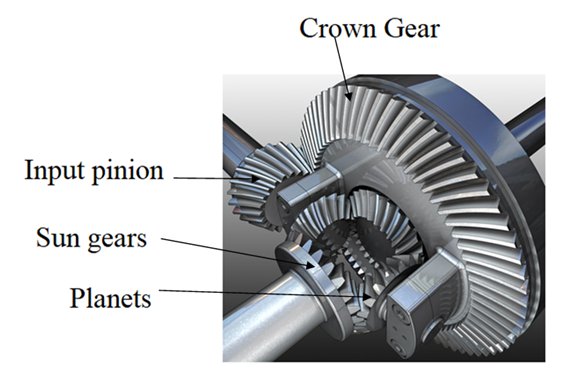
What are the applications of differential gears in off-road vehicles?
Off-road vehicles rely on differential gears for various applications that enhance their performance and capability in challenging terrains. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Traction Improvement:
One of the primary applications of differential gears in off-road vehicles is to improve traction. Off-road terrain often consists of uneven surfaces, loose soil, rocks, mud, or deep snow, which can cause the wheels to lose traction. Differential gears, such as limited-slip differentials or locking differentials, help distribute torque to the wheels with better traction, reducing wheel slip and maximizing grip. This allows off-road vehicles to maintain forward momentum and conquer obstacles that would otherwise be difficult to navigate.
2. All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Systems:
Off-road vehicles commonly utilize differential gears in their all-wheel drive (AWD) systems. AWD systems distribute power to all four wheels, providing better traction and stability on off-road terrain. Differential gears enable power transfer between the front and rear axles, as well as between the left and right wheels on each axle, allowing for optimal torque distribution based on traction conditions. This helps improve overall off-road performance and control.
3. Articulation and Wheel Independence:
Off-road vehicles often encounter uneven terrain with varying degrees of wheel articulation. Differential gears play a crucial role in maintaining wheel independence, allowing each wheel to move up or down independently to better conform to the terrain. This ensures that the wheels maintain contact with the ground and enhances traction, especially when navigating over rocks, logs, or steep inclines.
4. Hill Climbing and Descending:
When climbing steep inclines or descending steep slopes, differential gears are essential for off-road vehicles. In these situations, differential gears help distribute torque between the wheels on each axle, allowing the wheels with better traction to propel the vehicle forward or provide controlled braking. This improves stability, prevents wheel slip, and enhances the vehicle’s ability to tackle challenging uphill or downhill sections.
5. Off-Road Racing:
In off-road racing, differential gears are utilized to optimize performance and handling. High-performance off-road vehicles often employ advanced differential systems, such as limited-slip differentials or torque vectoring differentials. These systems actively distribute torque to the wheels with better traction, improving acceleration, cornering ability, and overall vehicle dynamics in competitive off-road racing environments.
6. Rock Crawling and Trail Driving:
Off-road vehicles designed for rock crawling or trail driving heavily rely on differential gears. These vehicles require precise control and maximum traction in low-speed, technical situations. Differential gears, particularly locking differentials, are employed to ensure that both wheels on an axle rotate together, maximizing traction and allowing the vehicle to maneuver over challenging obstacles, such as large rocks, boulders, or deep ruts.
In summary, differential gears in off-road vehicles have several applications, including traction improvement, all-wheel drive systems, articulation and wheel independence, hill climbing and descending, off-road racing, rock crawling, and trail driving. These applications enhance the performance, control, and capability of off-road vehicles in demanding and rugged terrains.


editor by CX 2024-01-05